# Nacos解析
作者:Ethan.Yang
博客:https://blog.ethanyang.cn (opens new window)
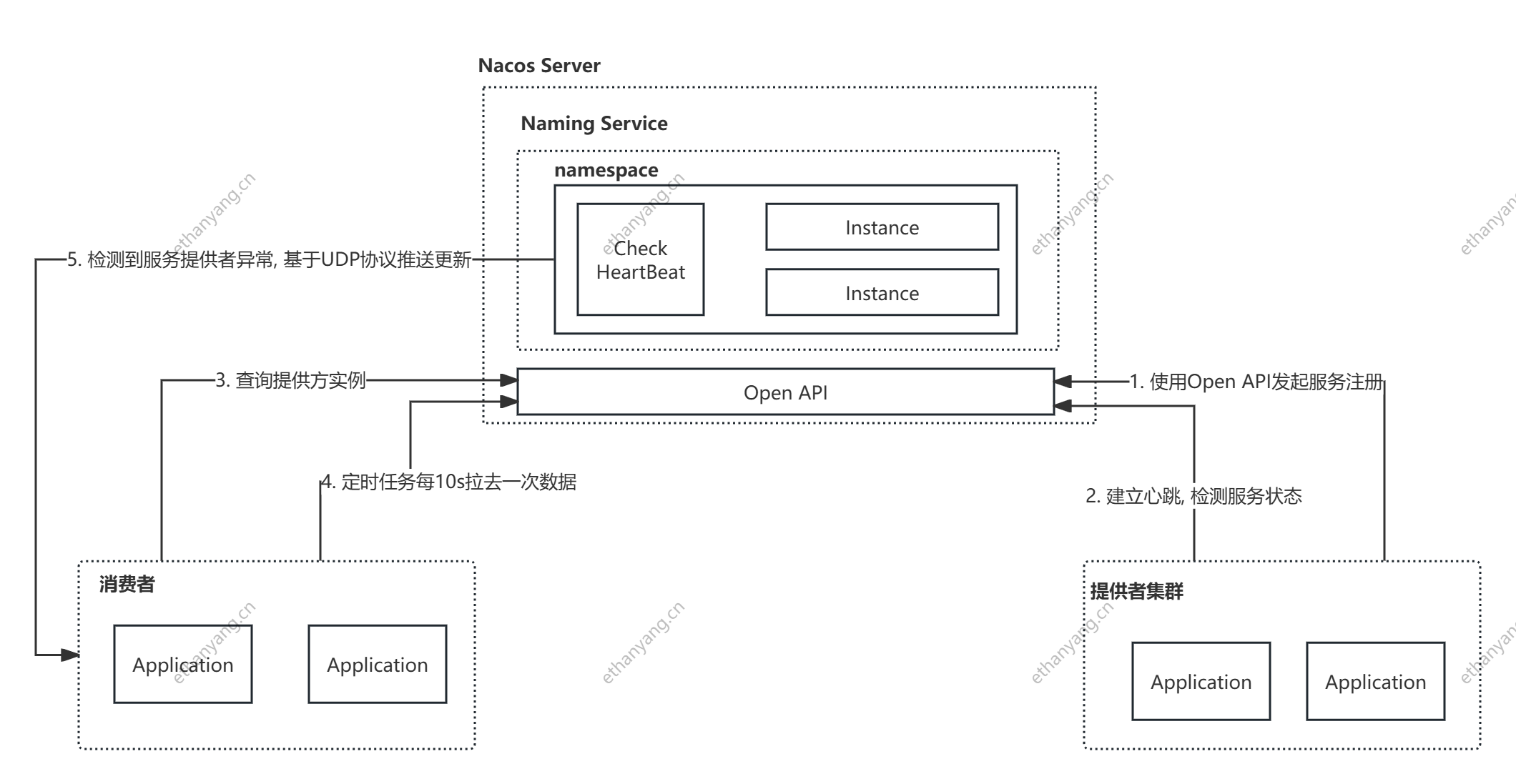
# 注册中心的原理
# 注册中心的功能
- 服务实例在启动时注册到服务注册表, 在关闭时注销。
- 服务消费者查询服务注册表, 获得可用实例。
- 注册中心需要调用服务实例的健康检查API验证服务是否存活。
# Nacos 注册中心源码
主要关注三部分源码:
- 服务注册
- 服务地址的获取
- 服务地址变化的感知
# 什么时候完成服务注册
spring-cloud-commons包中有这样一个接口ServiceRegistry, 它是spring-cloud对外提供注册的标准, 集成spring-cloud中实现服务注册的组件都会实现该接口。
package org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry;
public interface ServiceRegistry<R extends Registration> {
void register(R registration);
void deregister(R registration);
void close();
void setStatus(R registration, String status);
<T> T getStatus(R registration);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
spring-cloud-alibaba-nacos-discovery包中有NacosServiceRegistry接口, 用于注册功能, 实现了ServiceRegistry, 那么是在什么时机触发服务注册的动作?
# 集成 Nacos 的过程
spring-cloud-commons 中的META-INF/spring.factories中有自动装配的配置类, 关注下面这个配置类
org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@Import({AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
value = {"spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired(
required = false
)
private AutoServiceRegistration autoServiceRegistration;
@Autowired
private AutoServiceRegistrationProperties properties;
public AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration() {
}
@PostConstruct
protected void init() {
if (this.autoServiceRegistration == null && this.properties.isFailFast()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Auto Service Registration has been requested, but there is no AutoServiceRegistration bean");
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
在该配置类中, 注入了AutoServiceRegistration实例, 而Nacos的NacosAutoServiceRegistration继承了AbstractAutoServiceRegistration, 而AbstractAutoServiceRegistration继承了AutoServiceRegistration, 同时AbstractAutoServiceRegistration实现了ApplicationListener, 用来监听WebServerInitializedEvent事件, 当webServer初始化结束后调用this.bind(event), 在这个bind方法中会调用this.serviceRegistry.register(), 即调用NacosServiceRegistry的register方法。dubbo和feign都是通过自身的自动装配原理最终调用该方法进行服务注册。
public abstract class AbstractAutoServiceRegistration<R extends Registration> implements AutoServiceRegistration, ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent> {
// .........
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
this.bind(event);
}
// ......
2
3
4
5
6
# NacosServiceRegistry 的实现
public class NacosServiceRegistry implements ServiceRegistry<Registration> {
// .....
public void register(Registration registration) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(registration.getServiceId())) {
log.warn("No service to register for nacos client...");
} else {
String serviceId = registration.getServiceId();
String group = this.nacosDiscoveryProperties.getGroup();
Instance instance = this.getNacosInstanceFromRegistration(registration);
try {
this.namingService.registerInstance(serviceId, group, instance);
log.info("nacos registry, {} {} {}:{} register finished", new Object[]{group, serviceId, instance.getIp(), instance.getPort()});
} catch (Exception var6) {
Exception e = var6;
log.error("nacos registry, {} register failed...{},", new Object[]{serviceId, registration.toString(), e});
}
}
}
// .....
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
关注register方法, 其中调用了Nacos Client SDK提供的namingService.registerInstance方法完成服务的注册。
继续跟进registerInstance()
@Override
public void registerInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
if (instance.isEphemeral()) {
BeatInfo beatInfo = new BeatInfo();
beatInfo.setServiceName(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName));
beatInfo.setIp(instance.getIp());
beatInfo.setPort(instance.getPort());
beatInfo.setCluster(instance.getClusterName());
beatInfo.setWeight(instance.getWeight());
beatInfo.setMetadata(instance.getMetadata());
beatInfo.setScheduled(false);
long instanceInterval = instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval();
beatInfo.setPeriod(instanceInterval == 0 ? DEFAULT_HEART_BEAT_INTERVAL : instanceInterval);
// 1. 创建心跳信息实现健康检测
beatReactor.addBeatInfo(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), beatInfo);
}
// 2. 实现服务注册
serverProxy.registerService(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), groupName, instance);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
先关注心跳机制的实现即beatReactor.addBeatInfo(), nacos为每一个客户端建立发送心跳包的定时任务, 客户端会依照定时任务向nacos发送心跳包, 如果nacos长时间未收到, 则认为客户端出了故障
// 心跳包
POST /nacos/v1/ns/instance/beat
params:
serviceName=xxx
groupName=DEFAULT_GROUP
cluster=DEFAULT
ip=192.168.0.100
port=20880
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void addBeatInfo(String serviceName, BeatInfo beatInfo) {
NAMING_LOGGER.info("[BEAT] adding beat: {} to beat map.", beatInfo);
String key = buildKey(serviceName, beatInfo.getIp(), beatInfo.getPort());
BeatInfo existBeat = null;
if ((existBeat = dom2Beat.remove(key)) != null) {
existBeat.setStopped(true);
}
dom2Beat.put(key, beatInfo);
// 定时发送心跳包
executorService.schedule(new BeatTask(beatInfo), beatInfo.getPeriod(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
MetricsMonitor.getDom2BeatSizeMonitor().set(dom2Beat.size());
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 基于 Open API 源码分析Nacos服务注册
Nacos除了SDK的方式外, 还提供了Open API请求方式来实现服务注册。
curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=nacos.naming.serviceName&ip=1270.0.1&port=8082'
参考nacos源码: com.alibaba.nacos.naming.controllers.InstanceController#register
@RestController
@RequestMapping(UtilsAndCommons.NACOS_NAMING_CONTEXT + "/instance")
public class InstanceController {
// ....
@CanDistro
@PostMapping
public String register(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取serviceName
String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
// 获取 命名空间id
String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
// 调用注册实例
serviceManager.registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, parseInstance(request));
return "ok";
}
// ....
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
以1.中搭建案例为例, serviceName=sample-provider, namespaceId=public
**registerInstance()**注册实例
// Map<namespace, Map<group::serviceName, Service>> serviceMap (命名空间, <分组:服务名, 服务实例>), 服务实例包括了该服务名下的所有集群和实例
private Map<String, Map<String, Service>> serviceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void registerInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
// 1. 创建一个空服务, Nacos控制台服务列表中展示的服务信息, 初始化一个serviceMap
createEmptyService(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral());
// 2. 从serviceMap中根据namespaceId serviceName 获取一个service
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
if (service == null) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.INVALID_PARAM,
"service not found, namespace: " + namespaceId + ", service: " + serviceName);
}
// 3.添加服务实例
addInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral(), instance);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
createEmptyService
public void createEmptyService(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean local) throws NacosException { createServiceIfAbsent(namespaceId, serviceName, local, null); } public void createServiceIfAbsent(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean local, Cluster cluster) throws NacosException { // 1. 从serviceMap中根据namespaceId serviceName取出service Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName); // 如果缓存中不存在, 则创建并保存到缓存 if (service == null) { Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("creating empty service {}:{}", namespaceId, serviceName); // 创建服务 service = new Service(); service.setName(serviceName); service.setNamespaceId(namespaceId); service.setGroupName(NamingUtils.getGroupName(serviceName)); // now validate the service. if failed, exception will be thrown service.setLastModifiedMillis(System.currentTimeMillis()); service.recalculateChecksum(); if (cluster != null) { cluster.setService(service); service.getClusterMap().put(cluster.getName(), cluster); } service.validate(); // 2.将服务实例添加到缓存 putServiceAndInit(service); if (!local) { addOrReplaceService(service); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
311.1 putServiceAndInit
private void putServiceAndInit(Service service) throws NacosException { // 将服务缓存到内存Map putService(service); // 建立心跳检测机制 service.init(); // 实现数据一致性的监听 consistencyService.listen(KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName(), true), service); consistencyService.listen(KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName(), false), service); Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("[NEW-SERVICE] {}", service.toJSON()); }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
101.1.1 putService, 比较简单
public void putService(Service service) { if (!serviceMap.containsKey(service.getNamespaceId())) { synchronized (putServiceLock) { // 判断serviceMap是否包含NamespaceId, 不包含则创建Map<group::serviceName, Service> if (!serviceMap.containsKey(service.getNamespaceId())) { serviceMap.put(service.getNamespaceId(), new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16)); } } } // 向对应的Service添加服务实例 serviceMap.get(service.getNamespaceId()).put(service.getName(), service); }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
121.1.2 service.init() 心跳, 这边是nacos服务端建立心跳检查机制, 它会检查服务端最近心跳时间, 如果超时了则认为有故障, 并不是客户端向服务端发心跳包
public void init() { HealthCheckReactor.scheduleCheck(clientBeatCheckTask); for (Map.Entry<String, Cluster> entry : clusterMap.entrySet()) { entry.getValue().setService(this); entry.getValue().init(); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
addInstance 完成上述步骤后, 添加实例
# 服务提供者地址查询
上述分析完服务注册原理, 接下来查看服务地址查询功能, 当客户端启动时会通过SDK和nacos交互, 获取服务提供者的地址
curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=test
分析查询服务提供者地址的源码
@GetMapping("/list")
public JSONObject list(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 解析请求参数
String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID,
Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
String agent = WebUtils.getUserAgent(request);
String clusters = WebUtils.optional(request, "clusters", StringUtils.EMPTY);
String clientIP = WebUtils.optional(request, "clientIP", StringUtils.EMPTY);
Integer udpPort = Integer.parseInt(WebUtils.optional(request, "udpPort", "0"));
String env = WebUtils.optional(request, "env", StringUtils.EMPTY);
boolean isCheck = Boolean.parseBoolean(WebUtils.optional(request, "isCheck", "false"));
String app = WebUtils.optional(request, "app", StringUtils.EMPTY);
String tenant = WebUtils.optional(request, "tid", StringUtils.EMPTY);
boolean healthyOnly = Boolean.parseBoolean(WebUtils.optional(request, "healthyOnly", "false"));
// 返回服务列表
return doSrvIPXT(namespaceId, serviceName, agent, clusters, clientIP, udpPort, env, isCheck, app, tenant,
healthyOnly);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
doSrvIPXT 返回服务列表, 只用关注核心流程
public JSONObject doSrvIPXT(String namespaceId, String serviceName, String agent, String clusters, String clientIP,
int udpPort,
String env, boolean isCheck, String app, String tid, boolean healthyOnly)
throws Exception {
// 会移除很多无用代码
ClientInfo clientInfo = new ClientInfo(agent);
JSONObject result = new JSONObject();
Service service = serviceManager.getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
// ....
List<Instance> srvedIPs;
// 获取指定服务下的所有实例IP
srvedIPs = service.srvIPs(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.split(clusters, ",")));
// .....
Map<Boolean, List<Instance>> ipMap = new HashMap<>(2);
ipMap.put(Boolean.TRUE, new ArrayList<>());
ipMap.put(Boolean.FALSE, new ArrayList<>());
for (Instance ip : srvedIPs) {
ipMap.get(ip.isHealthy()).add(ip);
}
// ....
// 遍历, 完成JSON字符串的组装
JSONArray hosts = new JSONArray();
for (Map.Entry<Boolean, List<Instance>> entry : ipMap.entrySet()) {
List<Instance> ips = entry.getValue();
if (healthyOnly && !entry.getKey()) {
continue;
}
for (Instance instance : ips) {
// remove disabled instance:
if (!instance.isEnabled()) {
continue;
}
JSONObject ipObj = new JSONObject();
ipObj.put("ip", instance.getIp());
ipObj.put("port", instance.getPort());
// deprecated since nacos 1.0.0:
ipObj.put("valid", entry.getKey());
ipObj.put("healthy", entry.getKey());
ipObj.put("marked", instance.isMarked());
ipObj.put("instanceId", instance.getInstanceId());
ipObj.put("metadata", instance.getMetadata());
ipObj.put("enabled", instance.isEnabled());
ipObj.put("weight", instance.getWeight());
ipObj.put("clusterName", instance.getClusterName());
if (clientInfo.type == ClientInfo.ClientType.JAVA &&
clientInfo.version.compareTo(VersionUtil.parseVersion("1.0.0")) >= 0) {
ipObj.put("serviceName", instance.getServiceName());
} else {
ipObj.put("serviceName", NamingUtils.getServiceName(instance.getServiceName()));
}
ipObj.put("ephemeral", instance.isEphemeral());
hosts.add(ipObj);
}
}
result.put("hosts", hosts);
if (clientInfo.type == ClientInfo.ClientType.JAVA &&
clientInfo.version.compareTo(VersionUtil.parseVersion("1.0.0")) >= 0) {
result.put("dom", serviceName);
} else {
result.put("dom", NamingUtils.getServiceName(serviceName));
}
result.put("name", serviceName);
result.put("cacheMillis", cacheMillis);
result.put("lastRefTime", System.currentTimeMillis());
result.put("checksum", service.getChecksum());
result.put("useSpecifiedURL", false);
result.put("clusters", clusters);
result.put("env", env);
result.put("metadata", service.getMetadata());
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
# Nacos服务地址动态感知原理
客户端在首次获取地址列表后, 还需要实时的知道生产者地址列表的变动, 基本原理如下
- 客户端发起事件订阅后, HostReactor中有一个UpdateTask线程, 每10s发送一次pull请求, 获得服务端最新地址列表
- 服务端和服务提供者维持了心跳检测, 一旦服务提供者异常, 会push消息给Nacos客户端, 也就是服务消费者
- 服务消费者收到请求后, 使用HostReactor中解析消息, 并更新本地服务地址列表
# 配置中心
# springCloud Nacos配置中心基本使用
# 基本使用
参考项目根目录/nacosConfig项目
注意点
- 需要有bootstrap.yml文件存放Nacos配置信息, 该文件是优先于application.yml加载, 项目启动时需要加载Nacos配置信息
- Ncos控制台配置管理新增配置
- prefix表示Nacos控制台配置列表的Data Id
测试案例
@SpringBootApplication
public class NacosConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(NacosConfigApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("++ NacosConfigApplication start ++");
String info = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("info");
System.out.println("nacos 配置info: " + info);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 动态更新配置
在配置中心上修改配置的值, 应用程序需要感知值的变化。
测试代码, 变更nacos配置
@SpringBootApplication
public class NacosConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(NacosConfigApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("++ NacosConfigApplication start ++");
while (true) {
String info = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("info");
System.out.println("nacos 配置info: " + info);
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Nacos Config 自定义 Namespace、Group 和 Data ID 配置详解
Namespace(命名空间)命名空间用于实现 配置隔离,常用于不同环境(开发、测试、生产)的区分或者多租户系统。
配置方式:
在 Nacos 控制台创建命名空间,获取对应的
namespace-id在
bootstrap.yml(或bootstrap.properties)中添加:spring: cloud: nacos: config: namespace: your-namespace-id # 是 ID,不是命名空间名称1
2
3
4
5
Group(分组)Group是在一个命名空间中对配置的再分组,默认是DEFAULT_GROUP,常用于:- 相同环境下不同项目配置的逻辑隔离
- 对某一类配置进行集中管理
配置方式:
在 Nacos 控制台中新建配置时填写 Group 名称
在
bootstrap.yml中添加:spring: cloud: nacos: config: group: CUSTOM_GROUP1
2
3
4
5
6多个微服务共享同一个命名空间,但配置不同
通常会结合业务线分组,如:
ORDER_GROUP、USER_GROUP
Data ID(配置标识)Nacos 中配置项的唯一标识,通常与
application-name和profile相关,格式如下:${prefix}-${spring.profiles.active}.${file-extension}1默认:
prefix = spring.application.namefile-extension = yml(或properties)
举例:
如果配置如下:
spring: application: name: nacos_config profiles: active: dev spring: cloud: nacos: config: file-extension: yml1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12那么会去加载:
Data ID: nacos_config-dev.yml1你也可以自定义
prefix:spring: cloud: nacos: config: prefix: custom-name1
2
3
4
5最终加载的就是:
custom-name-dev.yml1一般不同环境的集群都是分开的 命名空间用来区分不同项目, group区分不同项目的服务, Data ID为唯一标识
# Nacos Config 实现原理解析
Nacos针对配置管理提供了4种操作, 分别是获取配置 监听配置 发布配置 删除配置, 并且都提供了 SDK和Open API的方式进行访问。简单来说就是提供了对配置的CRUD 和 配置的动态监听。
# 配置的CRUD
服务端对配置进行存储以及持久化, 客户端只需要通过接口从服务器端查询到相应的数据然后返回
# 动态监听之Pull Push
客户端和服务端之间的数据交互有2种方式: Pull Push
Pull 表示客户端从服务端主动拉取数据
一般来说需要客户端定时从服务端获取数据, 当数据更新不频繁时客户端属于无效拉取, 当数据频繁更新时因为是定时拉取数据的实时性没法得到保证。
Push 服务端需要和客户端维持长连接, 如果客户端数量较多, 服务端需要耗费大量的内存资源来保存每个连接, 并且需要有心跳机制检查连接状态
Nacos采用的是长轮询机制, 客户端长轮询的方式定时发起pull请求, 检查服务端配置是否发生变化, 如果变化了则请求直接返回, 否则服务端会对这个请求挂起
# spring cloud如何实现配置的加载
Spring提供了Environment, 项目启动时会把配置加载到Environment中, 创建Bean时可以通过@Value将属性注入, 并且提供getProperty(String key)获取配置属性;
为了实现Nacos的动态配置加载, 需要将远程服务的配置加载到Environment, 当配置更新时需要将配置更新到Environment中
PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
该类是一个启动环境配置类, 其中有一个initialize方法会调用PropertySourceLocator.locate加载远程服务的配置信息, 具体的加载流程如下
Spring Boot启动时, 在SpringApplication.run执行时, 会初始化环境配置
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { // .... try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); // 初始化环境配置 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); // .... }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8prepareEnvironment方法会发布一个环境配置事件
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) { // .... listeners.environmentPrepared((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment); // ..... return (ConfigurableEnvironment)environment; }1
2
3
4
5
6BootstrapApplicationListener 会监听该事件
← Dubbo 解析